Flute
IT: flauto – FR: flûte – GER: Flöte
Properties
The flute is a cylindrical metal pipe 26-1/2 inches long with a 3/4-inch inner diameter. The player blows across the side hole (or embouchure) to cause the air in the pipe to vibrate. Pitches in the lowest octave are fundamentals on the flute.
Range and Natural Dynamics
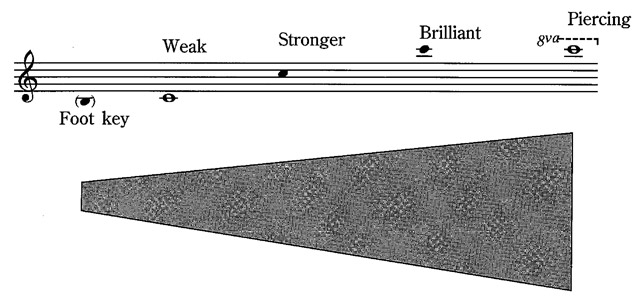
FIGURE 3.3 Flute range
The compass is from c1 upwards approximately three octaves, getting progressively brighter and more powerful. Most flutes have a foot key that adds 2 inches in length, enabling them to sound the b below c1.
Tone Quality
The flute’s pure tone quality, lacking in overtones, allows it to combine well with other instruments. Lower notes are breathy and upper notes penetrating; the range is otherwise quite even. It is easily covered unless exposed; notes in the lower octave may be overpowered when combined with several instruments pitched lower. Having a unique timbre, the flute is effectively used in its very low range when it does not have to compete with other instruments to be heard.
Technical Abilities
The flute is the most agile wind instrument, capable of wide leaps, filigree, arpeggios, trills, and rapid repeated notes. It requires a great deal of breath support and lip tension, so frequent rests are important for best results. Double-, triple-, and flutter tonguing (like a rolled “r”) are possible. Unplayable trills and tremolos are shown below:
 FIGURE 3.4 Unplayable trills
FIGURE 3.4 Unplayable trills
Piccolo
IT: ottavino
Half the size of the flute, the piccolo sounds an octave higher. The lowest note available is d1, and in the upper register it can become a shrill whistle.
Alto flute
Approximately one-third larger than the flute, the alto flute sounds a perfect fourth lower than written. It is sometimes called the G flute because the g below middle C is the pitch that sounds when a written c1 is played.
Bass flute
Rarely used except in flute choirs, it sounds an octave below written pitch.
 FIGURE 3.5 Piccolo, alto, and bass flute ranges
FIGURE 3.5 Piccolo, alto, and bass flute ranges
Musical Example
FIGURE 3.6 Flute line: Beethoven, Leonore Overture No.3, measures 328-337
See also the first movement of Dvorak’s New World Symphony in the Excerpts in Score section.