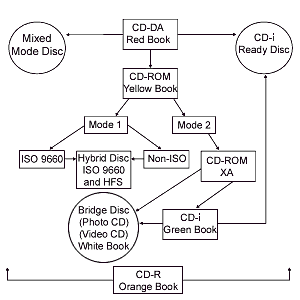
(n.) Originally the common term for a compact audio disc, now used freely to refer any optical disc 4.75 inches (12 cm) in diameter containing information encoded digitally in the constant linear velocity (CLV) format. The official designation for an audio CD is compact disc-digital audio (CD-DA). The accompanying illustration shows the evolution of compact discs and the relationship between different types of compact discs.
The following terms refer to specific types of CDs and CD formats:
CD-DA (n.) Compact disc-digital audio; the format used for high-fidelity music that offers a 90+ decibel signal-to-noise ratio and 74 minutes of digital sound. The standard for this format is the Red Book. Audio files are uncompressed 16-bit, 44.1-kHz samples.
CD+G (n.) Compact disc + graphics; developed by Warner New Media, this CD format is not readable by standard CD-ROM players. It includes extended graphics capabilities, as well as some limited video graphics written to the CD subcode area. The primary use is for karaoke, in which song lyrics are displayed and the music is played without vocals to accompany a person who sings the song. Pronounced “see-DEE plus GEE.”
CD-i (n.) Compact disc-interactive; developed in 1991 by Philips, a CD-ROM format that holds audio, digital data, still graphics, and MPEG video. These discs adhere to the Green Book standard. An infrared remote control device, a mouse, or a trackball allows users to interact with the content on the disc by clicking a cursor over hot spots on the video display.
CD+I audio levels (n.) Compact disc-interactive audio levels; levels of audio encoding that are part of the Green Book specification. Level A is a method of recording audio that offers fidelity comparable to that of standard CD audio, but it compresses the data to about half as much space on a disc. Level B is used in both the CD-i and CD-ROM XA formats; this method of recording audio offers medium fidelity but is more highly compressed than level A. Used in both the CD-i and CD-ROM XA formats, level C is a method of recording audio that offers fidelity sufficient for speech. It is highly compressed.
CD+MIDI (n.) Compact disc + Musical Instrument Interface; developed by Warner New Media, this CD format adds MIDI information to the digital audio data. Pronounced “see-DEE plus MID-ee.” See also Musical Instrument Digital Interface.
CD-plus (n.) A CD-ROM format from Sony and Philips that plays Red Book audio, written on the first tracks, and that includes graphics and data files readable by a microcomputer on later tracks. Windows 95 supports the CD-plus format.
CD-R (n.) Compact disc-recordable; developed in 1990 by Philips and Sony, it adheres to the Orange Book standard. It permits a CD recorder to write CD-DA, CD-ROM, CD-ROM XA, and CD-i block structures to a blank CD-ROM disc. The primary applications are for prototype production discs, or one-offs, and for archiving data. In 1992, a second generation of CD recorders became standard. They are capable of multisession recording, or writing additional information to a disc without deleting existing data. To read a multisession disc, readers must be able to identify a complex table of contents (TOC), but not all readers can do this. The original ISO 9660 logical file structure does not handle multisession discs, because it was created before their invention.
CD-ROM (n.) Compact disc-read-only memory; a 4.75-inch (12 cm) disc on optical memory storage is encoded. CD-ROMs hold about 650 megabytes (MB) of data. The standards for this format are called the Yellow Book. The logical level standard is called ISO 9660. The Unix extension is called the Rock Ridge Format.
tCD-ROM XA (n.) Compact disc-read-only memory extended architecture; an evolution of the standard CD-ROM format that provides for ADPCM audio, multisession discs, Photo-CD, and CD-i compatibility. This format relies solely on Cross-Interleaved Reed-Solomon Code (CIRC) for error correction.
CD-RW (n.) Compact disc-rewritable; a recordable CD-ROM that may be written over many times. It uses a different medium from a CD-R, which may be recorded only once.
CD-WO (n.) Compact disc-write once; another name for CD-R.